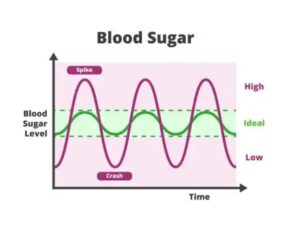
A sugar spike, also known as a sugar rush, is a term used to describe a sudden and temporary increase in blood sugar levels after consuming a large amount of sugar or high-glycemic carbohydrates. This can happen when someone consumes sugary foods or drinks, such as candy, soda, or desserts.
When a person consumes sugar, it is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream, causing a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. This can lead to a burst of energy and a feeling of heightened alertness. However, this energy boost is short-lived and is typically followed by a crash in energy levels.
During a sugar spike, the body produces more insulin to regulate the high blood sugar levels. Insulin helps to move glucose from the blood into the cells for energy or storage. When the body produces too much insulin in response to a sugar spike, it can result in a rapid drop in blood sugar levels, known as hypoglycemia. This can cause symptoms such as fatigue, shakiness, irritability, and lightheadedness.
Repeated sugar spikes and crashes can have negative effects on health, including weight gain, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic disorders. It is important to have a balanced diet that includes moderate amounts of sugar, complex carbohydrates, and other nutrients to help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Causes of Sugar Spike
There are various causes of sugar spikes, which refer to sudden and significant increases in blood sugar levels. Some common causes include:
1. Consumption of high-sugar foods: Consuming foods that are high in sugar, such as sweets, soft drinks, and desserts, can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels.
2. Carbohydrate-rich meals: Consuming meals that are high in refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, pasta, and rice, can lead to quick elevation of blood sugar levels.
3. Lack of physical activity: A sedentary lifestyle and lack of regular exercise can contribute to sugar spikes as the body is unable to effectively use and regulate blood sugar.
4. Insulin resistance: Insulin resistance occurs when cells in the body become less responsive to insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. This can result in higher blood sugar levels.
5. Stress: Elevated stress levels can cause the body to release stress hormones like cortisol, which can increase blood sugar levels. Additionally, stress may also lead to overeating or unhealthy food choices, further contributing to sugar spikes.
6. Certain medical conditions: Some medical conditions like diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and metabolic syndrome can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels properly.
It’s important to manage blood sugar levels to prevent complications associated with consistently high blood sugar levels, such as diabetes, heart disease, and kidney problems.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a sugar spike, also known as hyperglycemia or high blood sugar, may vary depending on the individual and the severity of the spike. Some common symptoms include:
1. Excessive thirst: Increased sugar levels can make you feel thirsty and increase your frequency of urination.
2. Frequent urination: High blood sugar levels may cause your kidneys to work harder to remove the excess glucose from your body, leading to more urination.
3. Fatigue: When your cells cannot effectively use glucose for energy, you may feel tired and lacking in energy.
4. Increased hunger: Despite having high blood sugar levels, your body’s cells are unable to get the glucose they need, triggering hunger signals.
5. Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can affect the fluid levels in your eyes, leading to temporary blurred vision.
6. Dry mouth: Elevated blood sugar levels can cause dehydration, resulting in a dry mouth.
7. Slow wound healing: High sugar levels can impair blood circulation and damage nerves, leading to delayed wound healing or frequent infections.
8. Recurrent infections: High blood sugar levels weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to frequent infections, particularly urinary and yeast infections.
9. Difficulty concentrating: Fluctuating blood sugar levels can affect brain function, making it difficult to concentrate or think clearly.
10. Numbness or tingling in extremities: High blood sugar can damage nerves, leading to tingling or numbness in the hands, feet, or other extremities.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to check your blood sugar levels and consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and appropriate management.
Health risks
Consuming excessive amounts of sugar can lead to several health risks, including:
1. Weight gain and obesity: Sugary foods and drinks are often high in calories but lacking in nutrients. Consuming too much sugar can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of obesity.
2. Type 2 diabetes: High sugar intake can lead to insulin resistance, which can eventually progress to type 2 diabetes. Regularly experiencing sugar spikes can disrupt insulin production and affect blood sugar control.
3. Cardiovascular diseases: A diet high in added sugars has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and inflammation in the body.
4. Increased risk of chronic diseases: High sugar intake has been associated with an increased risk of chronic conditions such as fatty liver disease, certain types of cancer (such as pancreatic and colorectal cancer), metabolic syndrome, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
5. Dental problems: Regularly consuming sugary foods and drinks can contribute to tooth decay and cavities. Bacteria in the mouth feed on sugars, producing acids that damage tooth enamel.
6. Mood swings and mental health issues: Sugar spikes can contribute to mood swings, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Additionally, some studies suggest a link between high sugar intake and a higher risk of mental health issues such as depression and anxiety.
It’s important to note that these risks are associated with excessive sugar consumption over time. Moderation and balance are key when it comes to sugar intake for maintaining good overall health.
Managing sugar spikes
Here are some strategies for managing sugar spikes:
1. Eat balanced meals: Include a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in your meals to slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing sudden spikes.
2. Choose complex carbohydrates: Opt for whole grains, legumes, and vegetables instead of highly processed carbs like refined grains and sugary snacks. Complex carbohydrates take longer to digest, which helps regulate blood sugar levels.
3. Portion control: Be mindful of portion sizes, especially when consuming foods high in carbohydrates. Eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day can help prevent sugar spikes.
4. Fiber-rich foods: Incorporate foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Fiber slows down digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
5. Regular physical activity: Engage in regular exercise or physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise routine.
6. Avoid sugary drinks: Limit or avoid sugary beverages like sodas, fruit juices, and energy drinks, as they can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Opt for water or unsweetened beverages instead.
7. Stay hydrated: Drinking enough water can help regulate blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 8 cups of water per day, or more if you are physically active.
8. Monitor your blood sugar levels: If you have diabetes or are at risk of developing diabetes, it is essential to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly. This will help you understand how different foods and activities affect your sugar levels and enable you to make informed choices.
9. Reduce stress: Chronic stress can lead to elevated blood sugar levels. Incorporate stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies and activities you enjoy.
10. Seek professional advice: If you are struggling to manage your blood sugar levels or have a medical condition such as diabetes, consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian. They can provide personalized advice and guidance for managing sugar spikes effectively.